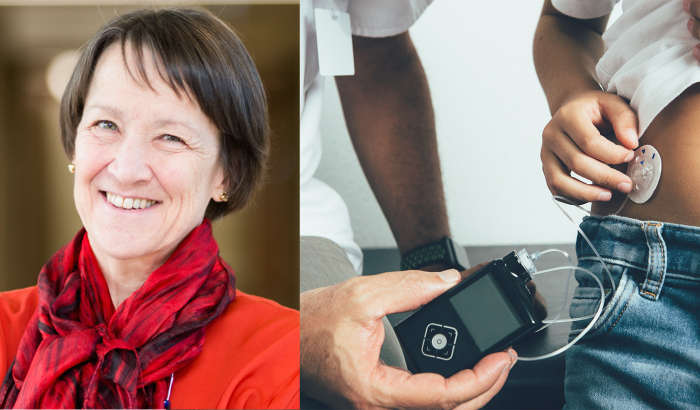
(C) Jonathan Turner, LIH)
Jonathan Turner and his research team
“However, stress is unhealthy when there is no time to recover and it becomes chronic” Jonathan Turner explains further. “Scientists have been showing for decades that people that suffer from chronic stress have a higher risk of developing, for example, diabetes, cancer, depression and cardiovascular diseases, to name a few.”
Long term consequences of childhood stress
One example of unhealthy stress is a stressful experience that occurs in early childhood. What are the long term consequences of a difficult childhood for our health? To explore this further, the Luxembourg Institute of Health has started a large investigation. They are investigating how and why childhood stress damages our health. They will look into cardiovascular risk factors, susceptibility to infections, psychological effects, and the stress response.
Young adults (18-35 years old) that spent a period of their childhood in an orphanage and/or were adopted can participate (register via epipath@lih.lu). Also people that had a stress-free childhood can participate as part of the control group.
Traumatic experiences in childhood can influence how the adult deals with stress
Adults are much better in dealing with stress than children. Early childhood is an especially vulnerable period, where stress has a much stronger impact. The impact is bigger than you might think. Traumatic experiences in early childhood can change the way we respond to stress for the rest of our lives.
“It seems that stressful experiences early in life shape your biological stress response, which makes it harder to recover from stress as an adult.” Already a few years ago, a large scale epidemiological study showed that childhood trauma can reduce your expected life span. The reduction is very strong and similar to the effect of lifelong smoking.
How is this possible?
How is this possible? One possible explanation is that perhaps childhood trauma unconsciously changes our behavior, and makes us live more unhealthy lives. Another possible explanation is that early trauma alters our response to stress, which increases the likelihood of becoming chronically stressed with all the health consequences that will entail.
Dr Jonathan Turner gives yet another explanation, “We believe that childhood stress makes fundamental changes in our biology via a mechanism called epigenetics.” Epigenetics is an upcoming field in science that can explain how our environment influences gene expression.
Author: LIH
Photo: Jonathan Turner and his research team (© Jonathan Turner, LIH)
Infobox
Epigenetics is a new research field, which studies the influence of the environment on our genes. Structural changes in the DNA, our hereditary material, could lead to the activation or inactivation of certain genes. If a gene no longer functions properly, the behavior of the cell or tissue could be altered.
EpiPath is a clinical study at the Luxembourg Institute of Health, carried out in collaboration with the University of Luxembourg and the University of Trier. The researchers involved in the study try to understand, how separation experiences in early childhood influence the risk to develop cardiovascular disease, respiratory infections and mental health problems.
The LIH is looking for healthy participants aged 18-35:
1. Who were adopted at a young age
2. Who were raised by their biological parents (control group)
In addition, participants should have a good knowledge of German. Indemnity for participation: 150 EUR. If you are interested, you can contact the research team until the end of February 2016 by e-mailing EpiPath@lih.lu
Two visits:
First visit (approx. 5 hrs)
A number of tests
Tasks on the computer
Physiological measurements
Second visit (approx. 2 hrs)
Interview and questionnaires
Survey:
Monthly online questionnaire on your current health (5-10 mins)